Since the beginning of 2011, the price of major rare earths has risen more than five times. As a major country with rare earth reserves, China's understanding of rare earth strategic resources has undergone a long-term process. Under the background of strong science and technology and economic transformation, the state limits the export of rare earths while encouraging the rapid development of rare earth new materials and rare earth applications. As an important part of magnetic materials, NdFeB magnets have become mainstream products for high-end magnetic materials. China's NdFeB industry accounts for more than 80% of the world's total output, and its production value exceeds 60%. With the sharp increase in rare earth prices, the open market price of NdFeB has risen at the same time. Nearly 100% of the NdFeB producers are now shifting their cost pressures and becoming beneficiaries of the industry chain. Under the background of “energy saving and emission reductionâ€, the rapid development of industries such as wind power generation, new energy vehicles and energy-saving appliances has directly stimulated the demand for NdFeB products. Under the premise of long-term optimistic about the price of rare earth, the cost-transfer capability of NdFeB manufacturers is also optimistic. Change upstream and downstream supply and demand So far, China's rare earth industry has experienced nearly 50 years of development. Since 1985, China began to implement the export tax rebate policy for rare earth products until 1998. China has implemented a system of export quotas for rare earth products, and has included rare earth raw materials in the catalogue of prohibited commodities in processing trade. Even in 2000, China began to implement a mining quota system for rare earths, reflecting the country’s re-understanding of strategic resources for rare earths. In order to reflect its important strategic position and completely change the issue of cheap export of products, from 2007 onwards, the state's plan for the production of rare earths has been adjusted to be directive. After 2005, rare earth management policies were introduced intensively, especially since 2011. From the “Rare Earth Industrial Pollutant Emission Standards†to the “State Council’s Several Opinions on Promoting the Sustainable and Healthy Development of the Rare Earth Industry,†the government has vigorously rectified the chaos of the rare earth industry. In accordance with the “Several Opinions of the State Council on Promoting the Sustainable and Healthy Development of the Rare Earth Industry,†in accordance with the relevant policies restricting the export of “two high and one capital†products, while strictly controlling the total production and production of rare earths, strictly controlling rare earth metals, oxides, and salts Exports of primary products such as rare earth and ferroalloys, and restrictions on mining, production, consumption, and export should be implemented simultaneously. Overall consideration will be given to domestic resources, production, consumption, and international market conditions, and the total amount of annual rare earth export quotas will be reasonably determined. As an important strategic resource, rare earth has been increasingly valued by the country. Based on the sustainable development of rare earth industries, the State Council issued a document in May this year to clarify the industry development goals, namely, to establish a standardized and orderly development of rare earth resources, smelting and separation, and market circulation order, with resource exploitation in a 1-2 year period. Blind expansion of production is effectively curbed, and the pattern of rare earth industries dominated by large enterprises is basically formed. We will improve the management of rare earth mandatory production plans, establish reserves of rare earth resources, and vigorously develop rare earth applications. In the context of industry-limited production and export restrictions, the domestic rare earth production system has undergone a relatively large amount of bending, and prices have shown an explosive growth trend. The price of major rare earths has risen more than 5 times since the beginning of the year. In the context of a powerful country with strong science and technology and economic transformation, the state limits the export of rare earths and encourages the rapid development of new rare earth materials and rare earth applications. In order to promote the technical progress of domestic rare earth materials systems, the State Council issued the "Decision on Accelerating the Cultivation and Development of Strategic Emerging Industries" in October 2010, explicitly making great efforts to develop new materials such as rare earth functional materials, and upgrading rare earth functional materials to a strategic height. As an important component of magnetic materials, NdFeB has high magnetic energy product, high coercive force, high remanence and other characteristics, and has become a mainstream product of high-end magnetic materials. China's high-performance NdFeB permanent magnet materials have seen a rapid growth over the past decade. In terms of global proportion, China has exceeded 80% of the world's total production, and 60% of its output value. Europe and the United States only account for 1%-2% in terms of output and output value. As the largest exporter of rare earths in China, Japan, based on the substantial adjustment of China's rare earth policy, will accelerate the transfer of rare earth downstream production capacity to China. Coupled with the expiry of formula patents in 2014, the rapid development of China's rare earth materials industry, especially the high-end rare earth industry, will be an inevitable trend. NdFeB cost components include material costs, energy costs, and a small amount of labor costs. Among them, the material cost accounts for 70%-80% of the overall cost. In the composition of the material cost, the proportion of rare earth metal or rare earth alloy including niobium, tantalum, and niobium iron accounts for more than 90%. As the price of rare earth continues to rise, its impact on the cost of NdFeB has become increasingly prominent. Increased price transfer capability Since the price of rare earths rose sharply in 2011, the open market price of NdFeB has basically risen synchronously. This correlation shows that so far, nearly 100% of NdFeB producers have shifted their cost pressures. The reason why 100% can be passed on to downstream customers is as follows: 1) In terms of product features, rare earth permanent magnets have high remanence, high coercive force, and high magnetic energy product characteristics and surpass other existing magnetic materials in performance. Rare-earth permanent magnets also have the advantage of high energy density, making it possible to miniaturize, lighten, and thin the instrumentation, electro-acoustic motors, and magnetic separation magnetization equipment. 2) From the perspective of application trends, rare earth permanent magnets are irreplaceable in their core areas. Although ferrite is still the most used magnetic material, the output value of NdFeB magnets exceeded that of ferrite permanent magnets in 2000. NdFeB is still irreplaceable in many fields of strong electricity. 3) From the perspective of manufacturers, high-performance NdFeB producers are relatively concentrated. The fullness of its orders indicates that downstream demand has not shrunk due to price changes. There are three possible changes in the rare earth price. Under the trend of different prices, the price of NdFeB and its supply and demand may have the following impact. First, prices continued to climb and hit new highs during the year. Based on this judgment, NdFeB producers may 1) continue to adopt a high inventory strategy. 2) Increase the shipping price accordingly based on matching costs. 3) In terms of financial impact, it will help to increase related company business income and gross profit margin. However, it may have a negative impact: 1) Some downstream industries and enterprises may not be able to bear the pressure of continued upward pressure on prices and do not rule out the reduction of purchasing scale. 2) Some of the cost-sensitive manufacturers may turn to the ferrite magnetic material technology system to replace NdFeB. Second, the price has declined in the short term, but it is still higher than the average price in two quarters and maintains a long-term upward trend. Based on this judgment, NdFeB manufacturers may 1) reduce stocks in the short term to reduce the impact of rare earth price adjustments on company stocks. 2) Because the price is bullish for a long time, the manufacturers will continue to expand their production capacity to meet the new downstream applications. 3) In terms of financial impact, short-term income and gross profit margin remained relatively stable. This situation may affect the procurement progress of downstream manufacturers of magnetic materials, but will not change the mainstream of rare earth permanent magnet downstream applications. Third, prices have fallen sharply on the current basis, falling below the average price in two quarters. Then 1) NdFeB manufacturers have asset impairment risks. 2) NdFeB customers may reduce inventory due to material price fluctuations. 3) The short-term finances of NdFeB manufacturers will be damaged, and both revenue and gross profit margin will be affected. Emerging application space is constantly magnified VCM, mobile phones, and consumer electronics are the traditional demand markets for NdFeB. Among them, only TDK, its annual demand for NdFeB is close to 4,000 tons. As the world's largest mobile phone production base, the demand for high-performance neodymium-iron boron in domestic mobile phones has steadily increased. In 2010, the output of mobile phones in China was 998 million units, corresponding to a demand of about 2,500 tons of high-performance NdFeB permanent magnet materials. The annual demand for high-performance NdFeB permanent magnet materials for consumer electronics, including DVD players and optical disc drives, exceeds 1,500 tons. NdFeB is widely used in the traditional fields of electronic information including mobile phones, PCs, audios, etc., and it is also developing in new fields such as new energy, energy saving and environmental protection. Under the background of “energy saving and emission reductionâ€, the rapid development of industries such as wind power generation, new energy vehicles and energy-saving appliances has directly driven the demand for NdFeB products. As a clean and sustainable energy source, wind energy is becoming an important part of many countries’ energy sustainable development strategies. According to the statistics of the Global Wind Energy Council, the global wind power industry has grown at an average annual rate of 28%. From the perspective of wind turbine technology, direct-drive permanent magnet wind turbines have become an important development direction for wind power technology because of their advantages such as high power generation efficiency, long service life, high stability, and simple structure. According to the "Twelfth Five-Year Plan", the total new installed capacity in 2011-2015 will exceed 250 million kilowatts. If 50% of them are direct-drive permanent magnet wind generators, the corresponding number of newly added machines is 75,000 units, and the use of sintered NdFeB materials will exceed 75,000 tons. With the increasingly stringent environmental protection measures in various countries in the world, new energy vehicles are receiving widespread attention due to their features of energy conservation and environmental protection. In 2009, relevant Chinese authorities began to promote new energy vehicles in some regions. In this context, domestic hybrid vehicles have entered a stage of rapid development. According to third-party estimates, during the 12th Five-Year Plan period, the cumulative number of new hybrid vehicles in China will exceed 8 million. With about 5KG of high-performance neodymium-iron-boron permanent magnet materials for each hybrid vehicle motor, the demand for high-performance neodymium-iron boron for hybrid vehicles will reach 7,500 tons by 2014. In home appliances, air conditioners are products that consume a higher proportion of energy. Inverter air conditioners are very popular in developed countries. In Japan, inverter air conditioners account for 97% of the total air conditioners. Although China's air-conditioning output has exceeded 100 million units, but the current output of inverter air conditioner is only 24 million units. Inverter air conditioner rare earth permanent magnet frequency conversion motor accounts for about 50%. With the improvement and mandatory implementation of the national standard for inverter air conditioners, it is expected that China's inverter air conditioners will maintain a compound growth rate of more than 30% in the next five years. The elevator is one of the largest energy-consuming equipment for high-rise buildings. China has become the world's largest elevator manufacturing base, the largest elevator market and the world’s second largest number of elevators. Energy-saving elevators using permanent magnet synchronous traction machines will be the future development direction of the elevator industry. In addition, rare earth permanent magnet materials also have a lot of demand in medical, robotics, CNC machine tools and other fields. With the neodymium iron boron component = patent expires in 2014, the overseas market will become an important market for domestic permanent magnet material manufacturers.
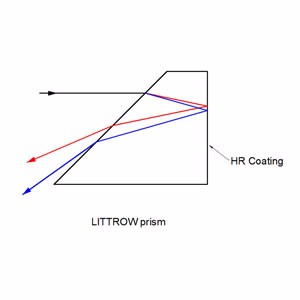
Littrow prisms feature 30°, 60°, and 90° angles .30° - 60° - 90° Littrow Dispersion Prisms can be used for a variety of applications. Uncoated littrow dipersion prisms are used to disperse light into its component spectrum. Coated littrow dipersion prisms are used to deviate the line of sight by 60°.
Dispersion Prisms (Uncoated)
Dispersion Prism,Optical Dispersion Prisms,Beam Deviation Prisms,Inked Dispersion Prism China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.opticsrealpoo.com
Collimated white light enters into the A-C surface of the prism, is reflected at the hypotenuse surface, and then dispersed into its component spectrum at the B-C surface. Although Littrow prisms produce narrower dispersion than equilateral prisms, Littrow prisms are typically less expensive.
Beam Deviation Prisms (Coated)
Incident light enters into the aluminum coated B-C surface of the prism at the nominal angle and returns back using the same path. In spectrum dispersion applications utilizing white light, the resolution performance of Littrow prisms is equal to equilateral prisms since the optical path length through the glass substrate is the same distance round-trip. Additionally, light entered into the A-C surface will reflect twice inside the glass substrate before being emitted through the hypotenuse surface at 60°.
Rare earth limited production of NdFeB