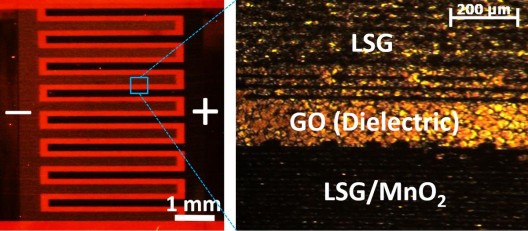
The scientific team at the California Nanotechnology Institute of the Greater Los Angeles campus (UCLA) has developed a new type of hybrid supercapacitor: it has a high-energy-density battery pack and fast charge-discharge characteristics. Compared with the current commercial supercapacitors, the hybrid supercapacitor has an energy density as high as six times that of the former, and the unit volume of electricity is comparable to or even higher than that of the lead-acid battery, but it has a high charge-discharge rate that the battery pack does not have. A hybrid supercapacitor with all these excellent features may improve the current state of the battery technology, apply to lightweight compact electronic devices, and electrically-powered vehicles that achieve high-speed charge and discharge in seconds and have similar reserve capacity to the battery pack. The high-performance hybrid supercapacitor project is led by Prof. Richard Kaner and Dr. Maher El-Kady. Like other supercapacitors, it can quickly realize charge and discharge, and has more than 10,000 cycles of charge and discharge cycles. However, the density of the stored electrical energy can be up to six times the capacity of an ordinary supercapacitor, and a 1/5 paper thickness hybrid supercapacitor can store 2 times the capacity of a thin film lithium battery of the same volume. The intensity of the storage capacity of the super capacitor depends on the contact area of ​​the electrolyte (liquid) between the electrodes of the device, and the larger the contact area, the higher the storage density. Early hybrid supercapacitors used a porous structure to maximize the contact area, but due to the large gap between the holes, the performance efficiency was greatly reduced. Under the leadership of Prof. Kaner and Dr. El-Kady, the research team improved the use of manganese dioxide electrodes and used a special 3D laser-etched graphene (LSG) material, which has high electrical conductivity and porosity. And the maximum surface area is designed so that the energy density is greatly increased. "The electrodes are very thin (about 15 microns), but this LSG/manganese dioxide electrode capacitor structure can store much more charge than a 100-200 micron thick commercially available supercapacitor, with much higher energy density." El- Dr. Kady said so. According to the team's claim, the new hybrid supercapacitor energy density can reach 42Wh/L, while the commercially available supercapacitor is 7Wh/L and the charge density can reach 10 kW/L. The team is further developing how to mass produce hybrid supercapacitors.
Natural Graphite , as its name implies, is naturally formed by natural Graphite , which is generally found in graphite schist, graphite-gneiss, graphite-bearing schist and metamorphic shale.
Features
The chemical composition of graphite is carbon (C). Naturally produced graphite is rarely pure and often contains impurities, including SiO2, Al2O3, MgO, CaO, P2O5, CuO, V2O5, H2O, S, FeO and H, N, CO2, CH4, NH3, etc. Natural graphite minerals are black, steel gray, striated black; Metallic luster, crypto, dull, opaque; The hardness is isotropic, the vertical cleavage surface is 3 ~ 5, the parallel cleavage surface is 1 ~ 2; Qualitative soft, density is 2.09 ~ 2.23 g/cm3, have the feeling of greasy, easy to contaminate finger. Mineral chip under the transmitted light is generally not transparent, extremely thin can pervious to light, the light green gray, refractive index of 1.93 ~ 2.07, under the reflected light is light gray, reflective pleochroism, Ro gray with brown, Re dark blue gray, reflectivity Ro23 (red), Re5.5 (red), the reflected color, double reflection were significantly, strong heterogeneity, polarization color for straw yellow.
Graphite is a complex six-party double cone, assumes the six-party tabular crystal, common simplex are parallel double, six-party double cone, hexagonal prism, but in good condition with rare crystal forms, the generally show scaly or platy, aggregate density lump, earthy or globular.
Type
The process performance and usage of graphite is mainly depends on the degree of crystallization, in accordance with its natural Graphite Crystal morphology can be divided into crystalline graphite, Flake Graphite ) and aphanitic graphite (earthy graphite) two types of industry.
Crystalline graphite
In the crystalline (scale) graphite ore, the diameter of graphite crystals is greater than 1 mu m. Ore grade is low, but optional; The mineral associated with graphite is usually mica, feldspar, quartz, diopathic stone, diabase, garnet and a small amount of pyrite, calcite, etc., some of which have some useful components, such as rutile and vanadium. The ore is scales, grainy scales or granulocyte structures, flaky, flaky, or blocky structures.
Crystalline (scale) graphite is divided into High Purity Graphite, High Carbon Graphite, Medium Carbon Graphite and low Carbon Graphite according to the fixed carbon content.
The high purity graphite (fixed carbon content is greater than or equal to 99.9%) is mainly used for flexible graphite sealing material, nuclear graphite, instead of platinum crucible for chemical reagent melting and lubricant base material, etc.
High carbon graphite (fixed carbon content 94.0% ~ 99.9%) is mainly used for refractory materials, lubricant substrate, brush raw materials, carbon products, battery raw materials, pencil materials, filling materials and coatings, etc.
Carbon graphite (80% ~ 94% fixed carbon content) is mainly used for crucible, refractories, casting materials, foundry coatings, pencil raw materials, battery materials and dyes, etc.
Low carbon graphite (fixed carbon content 50.0% ~ 80.0%) is mainly used for foundry coatings.
Cryptocrystalline graphite
Cryptocrystalline graphite is also called soil graphite or amorphous graphite. In cryptocrystalline graphite ore, graphite crystals are less than 1 mu m in diameter, which are microcrystalline and can only be seen in the electron microscope. High grade of ore, but poor selectable; The mineral associated with graphite is often quartz and calcite; The ore is microscaly - cryptocrystalline structure, block or soil structure.
Cryptocrystalline graphite ore is mainly distributed in contact metamorphic deposits. Actually the diameter graphite flake graphite ore is uneven, the so-called crystalline graphite ore, may also contain the aphanitic graphite, are too many content is often referred to as the mixed type graphite ore, may also contain a small amount of aphanitic graphite quality mineral crystalline flake graphite piece diameter slightly larger than 1 microns.
Cryptocrystalline graphite ore is mainly used in pencil, battery, electrode, graphite emulsion, graphite bearing ingredients and the raw materials of battery carbon rod. The non-ferrous graphite is mainly used for casting materials, refractory materials, dyes and electrode paste.
Natural Graphite Natural Graphite,Expanded Graphite,Colloidal Graphite,Special Graphite Fengcheng Ruixing Carbon Products Co., Ltd , http://www.lnfcrxts.com

Increase the development of new hybrid supercapacitors