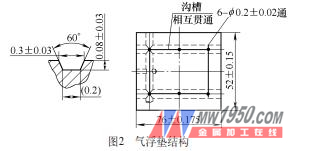
The air static pressure guide in the measuring machine is an important part of the three-dimensional movement of the coordinate measuring machine. The earliest developed three-coordinate measuring machine is mostly a sliding friction guide. Because of its large frictional resistance, it is easy to wear. The difference between the static and dynamic friction coefficients is large, and the measuring machine is prone to creep when it is low speed. To meet the ever-increasing accuracy and speed of measuring machines, sliding friction guides have gradually been replaced by air-static rails. The air static pressure guide has a small friction coefficient, stable operation, high motion precision and low wear, and has become the most widely used guide rail form in the current coordinate measuring machine. 1. How does the static pressure guide work? The moving parts and the guide members of the air static pressure rail are separated from each other by a gas film which is formed when compressed air is discharged from a gap between the air floating mat and the receiving surface. Such air float pads are typically arranged in a group of rails. Figure 1 is a working principle diagram of a common air floating cushion. The clean, dry and constant pressure compressed air sent from the gas source enters the air chamber through the throttle device and flows out along the sealing gas surface to form a gas film with bearing capacity between the sealing gas surface and the bearing surface. The sum of the bearing capacity of the gas film at the air chamber and the sealing surface floats the air floating mat and the work table connected thereto. The load capacity and load are in equilibrium during work to achieve gas friction. When the load is increased, the film thickness is decreased, and when the load is decreased, the film thickness is increased. On the one hand, the gas film acts as a load bearing and also plays a role in lubrication. 2. Specific structure and application requirements In this paper, the total weight of the Z-axis air cushion of the coordinate measuring machine is 204.74N, and the air floating cushion which plays the role in the Z-axis is 2, then the bearing weight of the single air floating cushion is 102.37N. The air cavity radius r1 of the air floating cushion structure design is 7mm, and the air float radius r2 is 38mm. According to the bearing capacity formula, the bearing weight is 134N, which is far greater than the maximum load 102.37N. According to the theoretical calculation, the structural air floating cushion shown in Figure 2 can fully meet the load requirements. In the design of the air floating cushion, it must also be fully considered that the imperfect design of the air floating cushion will cause the hammer to oscillate, which makes the instrument unstable. The volume ratio is the main cause of the air hammer oscillation. The volume ratio calculation formula shows that the volume ratio of the air floating cushion is 0.048, which satisfies the volume ratio requirement range of 0.02 to 0.05. The volume ratio design also meets the requirements, and gas does not occur. Hammer oscillation phenomenon. In practical applications, the characteristics of the air floating cushion are relatively complicated and affected by many factors. When the accuracy of the air-floating guide is high, the following practical factors must be considered: (1) The greater the supply pressure to the air bearing, the greater its load carrying capacity and stiffness. The general supply pressure is 0.3 to 0.6 MPa. (2) To increase the bearing capacity and rigidity of the air bearing can be achieved by increasing the number of orifices. The orifices are generally arranged in the middle of the air floating cushion. (3) Improving the characteristics of the air bearing can appropriately adjust the thickness of the film and the diameter of the orifice, which is simple and effective. Air bearings of the same size can reduce the stiffness of the bearing and reduce the diameter of the orifice. However, if the orifice is too small, it will become more difficult to manufacture and easy to block. Specific to the design of the air bearing should also consider the actual factors such as the use environment and processing level. (4) If the air bearing is tilted, the uneven film will reduce the rigidity of the air bearing, so try to avoid this phenomenon when using it. In the design of the air-floating guide rail, the air bearing in the same direction can be distributed as far as possible. In addition, the thickness of the gas film has a relatively large influence on the tilting effect of the bearing. When the thickness of the gas film is small, the change of the bearing capacity of the bearing is not sensitive to the inclination of the bearing; when the thickness of the gas film is large, the bearing capacity of the bearing is inclined. The rate increases and increases; the smaller the film thickness, the more sensitive the change in bearing stiffness is to the tilt of the bearing. (5) Under different film thicknesses, the variation of air bearing characteristics is inconsistent. Bearing characteristics at a film thickness are not necessarily correctly inferred from bearing characteristics at another film thickness. In practice, it is often necessary to use a suitable film thickness as required. 3. Conclusion The air floating cushion structure designed by this scheme has been applied and tested on the actual coordinate measuring machine. All technical indexes have met the design requirements, and the measuring machine runs smoothly and reliably, achieving the required precision. It can be seen that this design is feasible. This design has accumulated valuable experience in the design of various types of CMM air floating cushion structures. Apron Bathtub,Built-In Bathtub,Skirted Tub Freestanding Bathtub Shower Door Co., Ltd. , http://www.chabathtub.com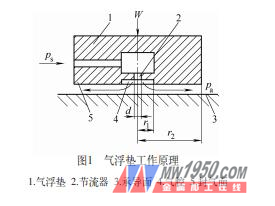
Design of air floating cushion in air static pressure guide of coordinate measuring machine