First, the turbidity of low-grade liquor In the production of low-alcohol liquor, due to the degradation of wine, the solubility of higher fatty acids, higher fatty acid ethyl esters, and other higher fatty acid esters in liquor is reduced, causing the wine to appear milky and turbid, which is a phenomenon of loss of light. Removing the precipitate from low-alcohol, maintaining the flavor of the original wine, low temperature without losing light is the key to producing low-grade liquor. Although there are many methods for removing turbidity, such as freezing method, starch method, resin method, anticoagulant method, calcium phosphate method, crystalline cellulose method, alcohol-based charcoal method, etc., the comprehensive comparison is best for alcohol-based charcoal method. The loss of ethyl hexanoate in Luzhou-flavor low-alcohol liquor is a key indicator affecting the flavor of wine. Different activated carbons are used, and the adsorption of ethyl hexanoate is also different. It has been determined that the molecular diameter of ethyl hexanoate is 14 . If activated carbon with a pore size of 14-20 is used to remove the precipitate from the low-grade liquor, ethyl hexanoate will enter the micropores and be adsorbed, which will damage the flavor of the low-alcohol liquor. Only the charcoal-specific charcoal with a pore diameter greater than 20 is used, and the micropores become channels of ethyl hexanoate, and the charcoal does not adsorb ethyl hexanoate. This is the reason why the special charcoal for the preparation of low-grade liquor can absorb precipitates, keep the low-alcohol low-temperature without losing light, and maintain the flavor of Luzhou-flavored liquor. In addition, activated carbon with a pore diameter of less than 14 is selected. Although ethyl hexanoate cannot enter the micropores and does not lose ethyl hexanoate, the adsorption of higher fatty acid ethyl esters and higher fatty acids with large ionic radius is less due to the small pores of the carbon. Less, we must increase the amount of carbon to ensure low temperature without losing light, which invisibly increases the processing cost of tons of wine, which is not enough for our company. For the fragrant liquor, the molecular diameter of the main scent ethyl acetate is 6•7, the range of activated carbon is wider, and the loss of ethyl acetate is also small. However, it should be noted that any type of activated carbon has a wide pore size distribution, is not absolute, and various pore sizes are present at the same time. Second, alcohol-specific charcoal accelerates the ripening of white wine, Chenhua new wine, the general taste is violent, spicy, noisy, and sometimes there is a new wine smell. In order to produce high-quality wine, it is necessary to have a certain storage period in the production process, ranging from three months to six months, and several years or more, known as the ripening and aging of wine. The process of ripening and aging is a comprehensive chemical-physical process. There are chemical changes such as oxidation, esterification, and acetylation, as well as physical and chemical effects such as molecular structure rearrangement. In the process of natural ripening, low-boiling substances such as aldehydes and sulfides volatilize, which removes the unpleasant smell of new wine; acetaldehyde condensation reduces the spicy taste; some higher alcohols decompose, making the liquor bitter and astringent, The spicy taste is reduced; the association of ethanol and water molecules increases the soft feeling of liquor; during the long-term storage of liquor, part of the ethanol is oxidized to acetaldehyde, part of which is further oxidized to acetic acid, and acetic acid further reacts with alcohol to form ethyl acetate. And higher fatty acid esters, a part of aldehydes and ethanol react to form acetals. Thereby reducing the spicy taste of the wine, increasing the aroma, and making the wine soft and soft. However, natural ripening and aging are a very slow process. Luzhou-flavor liquor is stored for at least half a year, while sauce-flavored liquor is stored for three years. Such a long cycle, the large area occupied by the wine cellar, the backlog of funds, correspondingly reduced the economic benefits of the winery. In order to overcome this problem and accelerate the aging of wine, various rapid old machines, aging machines, gamma rays, X-rays, ultrasonic waves, etc. have appeared on the market, but the effects are not good. It is only 1-3 days to treat the new wine with charcoal-specific charcoal (0•1%-0•3% of charcoal). The treated wine has a soft taste, less pungency and no new wine odor. The reason for chasing this is that the charcoal for charcoal is an oxidized charcoal with a large specific surface area, and there are many oxygen-containing functional groups and various trace metals and metal ions on the surface, and a small amount of charcoal-specific charcoal is in the wine. The large specific surface area and oxygen-containing functional groups are in full contact with the wine, and the charcoal-specific charcoal adsorbs some odor-producing substances (sulfide, higher fatty acid, etc.); the alcohol-specific char accelerates the oxidation of ethanol to make it acetaldehyde. Further oxidation to acetic acid, acetic acid and catalyzed the formation of ethyl acetate and higher fatty acid esters of alcohol and acetic acid, as well as other condensation reactions. It can be seen that after adding the special charcoal for alcohol, in a short period of time, the oxidation, condensation and deodorization of the new wine can be completed in the middle and long term. Third, remove the odor and bitterness in the wine Removing the odor from the wine is a unique adsorption of the large specific surface area of ​​the charcoal for charcoal. However, the odors in the wine are different, such as the sweetness of molasses alcohol, the smell of new wine, the new smell, and the bitterness of some wines. It is not effective to use a special type of charcoal, and it is only necessary to use special charcoal for different pore structures. The molasses sweetness is a large ionic radius material, which is effective with a large-pore alcoholic charcoal; the special smell of the new wine and the new astringency of the wine with a small pore size are obvious; for the bitterness of the wine, then It is necessary to use a special charcoal for alkaline alcohols with nitrogen-containing micropores. Other simple nitrogen-containing activated carbons or simple alkaline activated carbons cannot remove the bitterness of the wine. In summary, different charcoal-specific charcoal, used in different treatments of alcohol, have good results, which is the use of special activated carbon for alcohol. Different pore structure, different surface chemical composition, while paying attention to the pH value of charcoal-specific charcoal. Activated carbon is widely used in sugar, pharmaceutical, food and other fields. With the development of science and the emphasis on environmental pollution, activated carbon has stepped into sewage and gas treatment, which has further broadened the application fields. It is widely used in sewage treatment, gas treatment, water purification, and is mainly used for deodorization and iron removal. However, not only these in the wine industry, but also a multi-functional. It has a special role in the adjustment of the flavor of the wine and the sterilization of the aldehyde liquid. The application of activated carbon in the wine industry is summarized below. Although some are about the application of sake, it can also be used as a “stone of other mountains†for reference. Inappropriate points also ask the public in the country to criticize and correct. 1 The quality of the wine and the performance of the activated carbon are constantly changing. Therefore, the amount of activated carbon and the method of operation should be adapted to the specific situation and cannot be static. Today, the use of activated carbon at home and abroad is still an empirical figure. Therefore, it is necessary to go through a small test every time before it can be used for large production. 2 Activated carbon has different adsorption capacities for various wine ingredients. For example, flavanones and melanides are easily removed. It can remove dark brown wine into colorless and transparent. However, it is difficult to remove the glycine iron formed by the contact of iron with glycine in the wine. If you increase the dosage, you can only remove 50% one printing%. 3 The efficiency of activated carbon is not affected by the temperature, contact time, and the temperature of 20. The decolorization rate between the temperature and the temperature is not significantly different. The stirring is strengthened to make the activated carbon fully dispersed. The contact time lh is sufficient (the carbon content is different, and the sedimentation time varies greatly). It is necessary to know that the activated carbon is doubled and the adsorption rate is not twice as high. Therefore, increasing the amount of activated carbon does not receive the expected results, but it is counterproductive. 4 In the correction of wine taste, activated carbon is not very satisfactory for the treatment of rancidity and aroma. Only coconut shell activated carbon has a better effect. However, it has a significant effect on substances such as turbidity, mildew, odor, rubber odor, etc. (mainly refers to sake). 5 Activated carbon has a significant effect on the iron removal of brewing, but the key is to strengthen the water, water, container, filter material, etc. Water purification with powdered activated carbon removes iron, copper and zinc cations from water, and also has strong adsorption capacity for water odor, bleaching powder and grabbing. However, the calcium and magnesium ions that are beneficial to fermentation have poor adsorption capacity, which is of great benefit to winemaking. This is the biggest advantage of activated carbon. 6 Activated carbon, too much, staying in the wine for too long, the wine is prone to carbon, which is to dissolve the substances in the activated carbon into the wine. Some people tested 44 kinds of activated carbon, resulting in 35 kinds of unknown ingredients in the wine; 5 kinds of ethyl acetate added; 4 kinds of acetaldehyde increased. 7 Activated carbon adsorption in wine, 1 edge of the edge of a straight rise, 30 a print and n slightly increased, l 10h is basically flat, indicating that the time should not be too long. Increasing the agitation can increase the adsorption rate. Practice has proved that activated carbon stays in wine for a long time, and acetaldehyde and ethyl acetate are significantly increased. 8 Activated carbon has a strong adsorption to the odor in the air. Therefore, the activated carbon should be used up once after opening. If there is any remaining to prevent moisture absorption, it should be kept in a dry place, otherwise it will cause trouble.
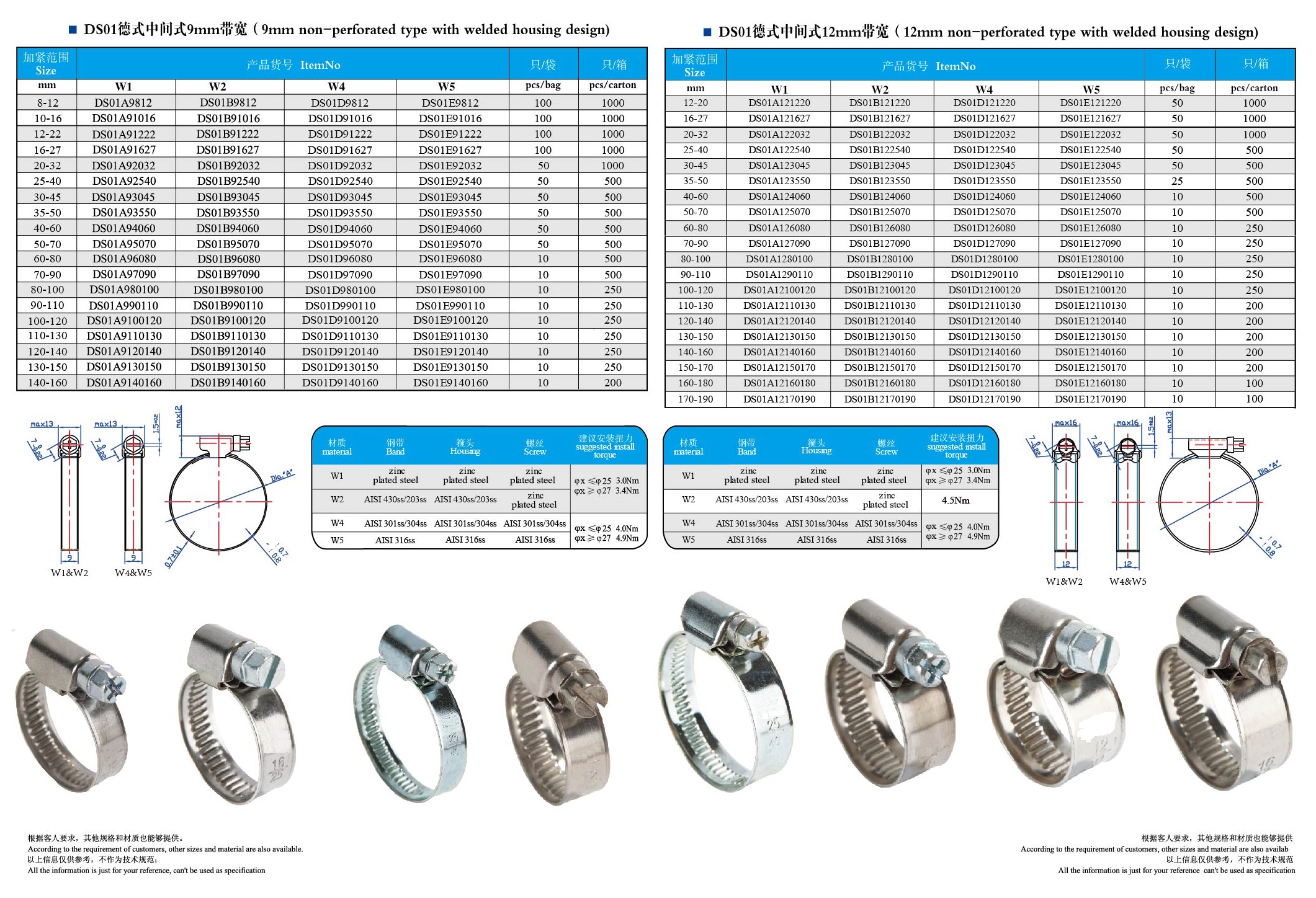
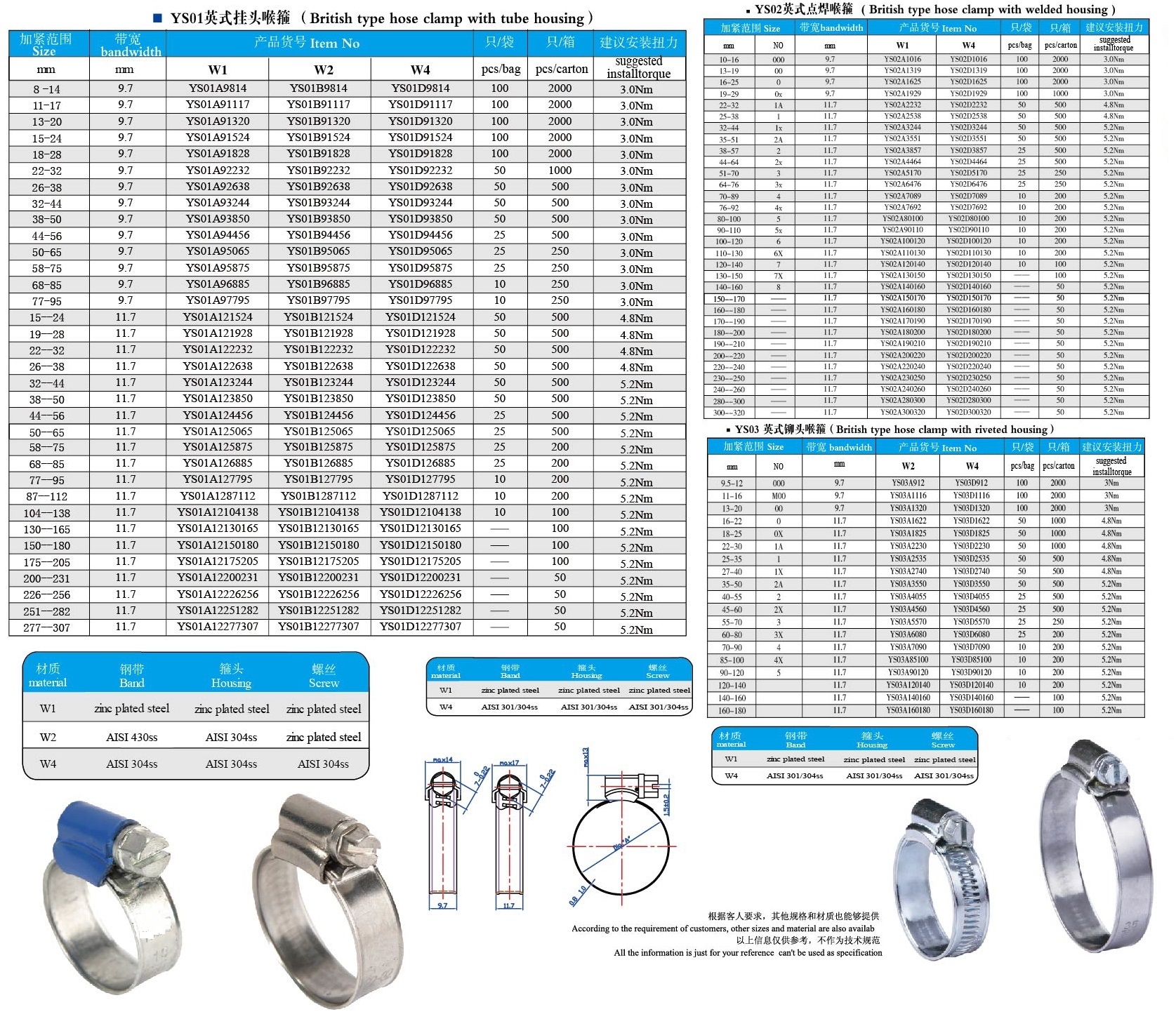
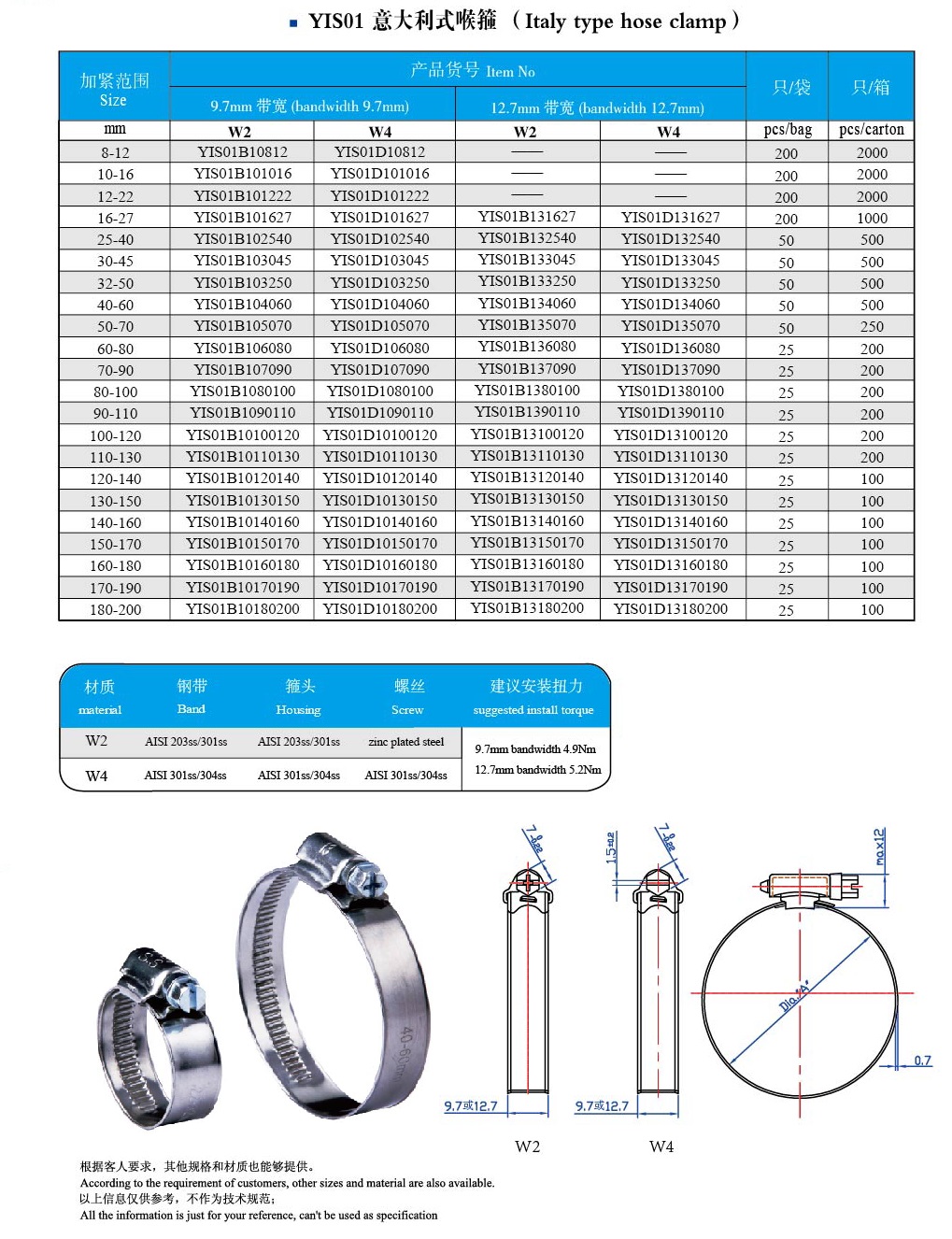
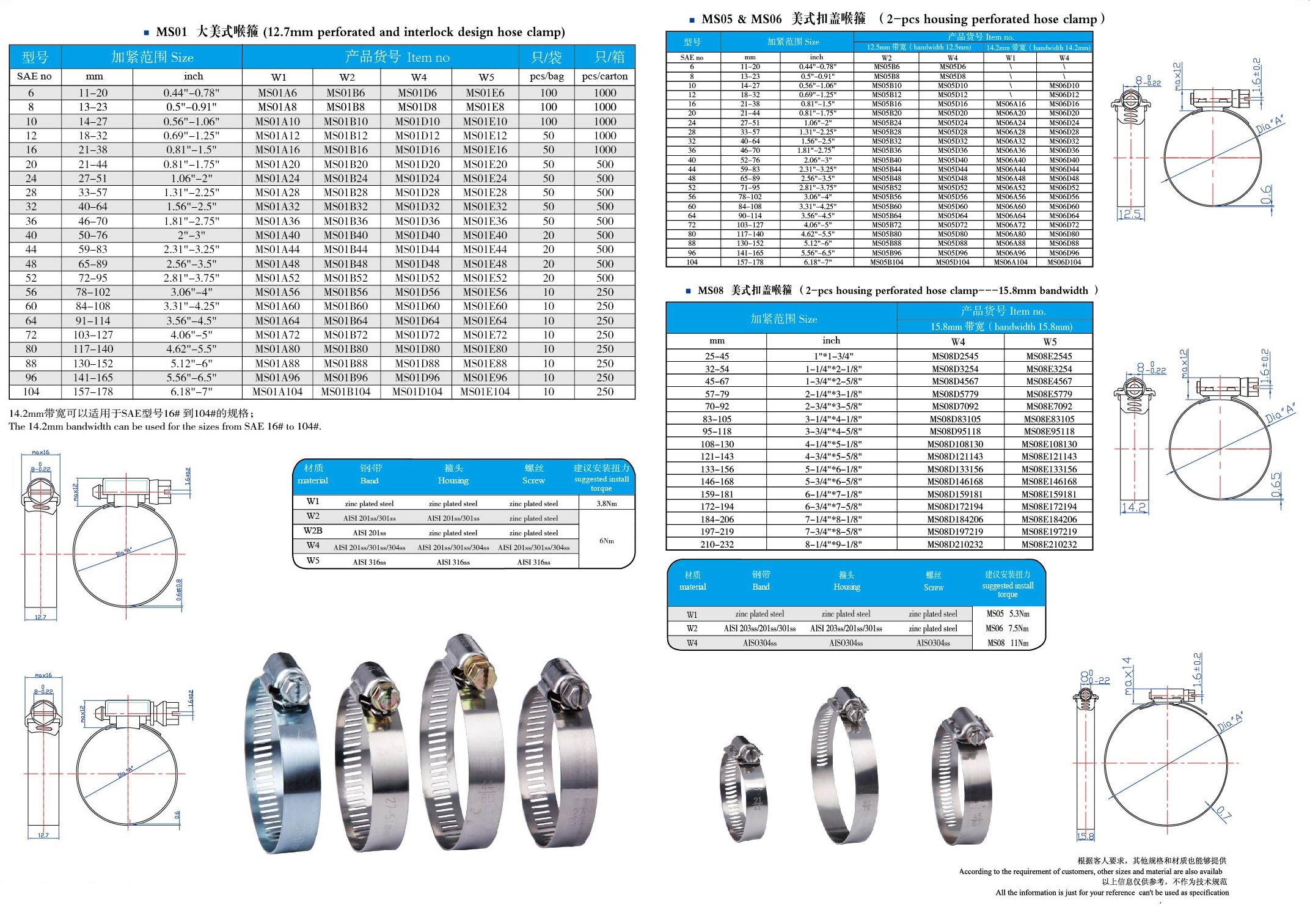
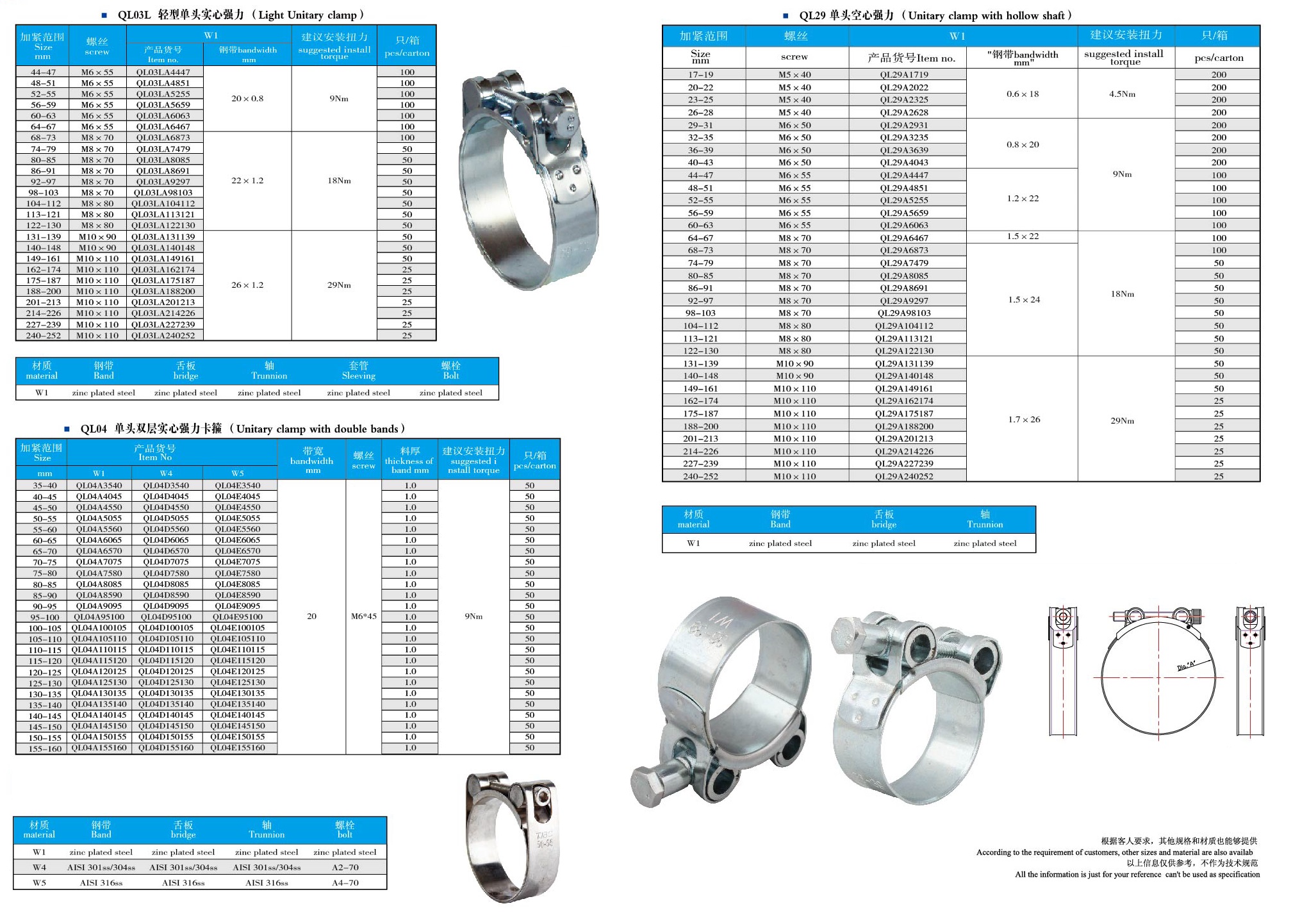
Item:Hose Clamps
Standard: British, America, Germany, Italy,T-Bolts and others
Material: Carbon steel, Stainless steel or as required
Finishing: Siler zinc coated or Yellow Zinc coated
Application: For industrial piping, agricultural irrigation, auto parts and other places for fixation.
Germany standard:
British standard:
Italy standard:
American standard:
T-bolt Clamps:
Hose Clamps Hose Clamps,Flexible Clamps,Stainless Steel Hose Clamps,Warm Drive Clamps HEBEI ZIFENG NEW ENERGY TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD. , http://www.zifengpipeline.com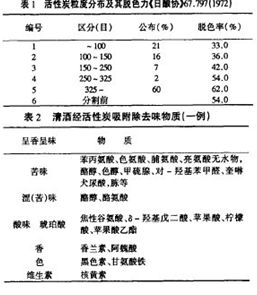

Discussion on the action mechanism of activated carbon for alcohol