The reporter learned from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences that Yang Weishen’s team has made important progress in the field of gas separation membranes recently and has prepared a gas separation “masterâ€â€”an ultra-thin MOF nanosheet film with a thickness of less than 10 nanometers. Pass hydrogen alone and leave unwanted carbon dioxide. The related results were published in the form of communication on the Angewandte Chemie International Edition. The so-called gas membrane separation technology refers to a high-efficiency separation process method in which the mixed gas passes through different membranes and is driven by a certain pressure difference to achieve the separation purpose. The phase change does not occur in the separation process. Yang Wei Shen said that gas membrane separation has lower energy consumption and less carbon emissions, and it is an efficient and energy-saving separation technology. The basis and core of membrane separation is membrane material. Polymers occupy the major share of the global membrane separation market with its advantages of easy molding and low cost. However, when the permeation flux of the polymer membrane is high, the separation selectivity is often low; when the separation selectivity is high, the permeation flux is not satisfactory, which seriously restricts the application of the polymer membrane. Professor Yang Weishen led the team to use metal-organic framework (MOF) as the research object. It was the first in the world to propose the use of two-dimensional porous nano-sheets for the construction of high-efficiency, ultra-breathable separation membranes, and tried to overcome this bottleneck. Yang Weishen’s research team selected a structurally stable laminar MOF precursor. Under mild physical external forces, the MOF nanosheets with monolayer thickness were first layer-exfoliated and then prepared using a self-developed thermal assembly method. Two-dimensional MOF nanosheets with ultra-high gas permeation flux and accurate molecular sieve capability. This achievement was published in 2014 in the world's top academic journal "Science" and received great attention and recognition from international counterparts. Recently, Yang Weishen team made new and important progress in the field of two-dimensional MOFs gas separation membranes. The research team selected a new amphiphilic layered MOF precursor Zn2 (Bim)3, which was first layered to obtain double-layered nanosheets. The ultrathin MOF nanosheet film with a thickness of less than 10 nm was prepared by a heat assembly method. More interestingly, due to the "preference" of the amphiphilic materials for carbon dioxide, the carbon dioxide molecules need to consume more energy through the membrane, so the membrane's transmissivity and mixing with hydrogen as the test temperature increases The gas separation selectivity increases at the same time, but the carbon dioxide flux is almost constant. It is not as low as the performance of other two-dimensional nanosheet membrane materials. According to Yang Weishen's team, this new type of amphiphilic MOF nanosheet not only has broad application prospects in the field of carbon dioxide pre-combustion capture, but also has important guiding significance for the selection of nano-sheet material in the future. (Reporter Qiu Chenhui) Condensing Unit,Air Con Condenser,Air Condenser Unit,Mini Split Condenser LONG TERM ELEC. CO., LTD , https://www.longterm-hvac.com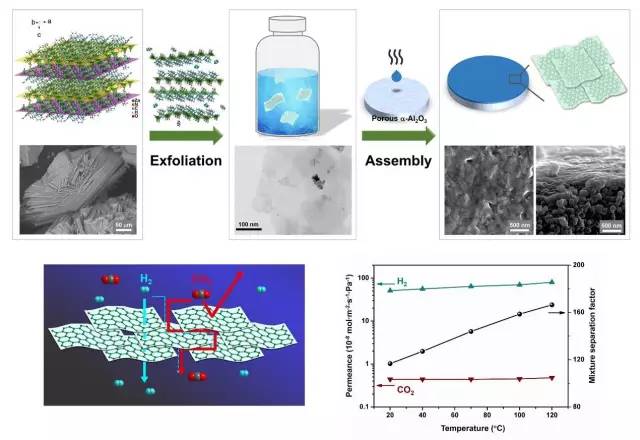
My scientists prepare gas separation "masters"