Recently, Li Can, academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Catalysis Fundamentals and Solar Energy Research Department, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Wang Xuxu, a professor at the School of Chemistry of Fuzhou University, have jointly developed a solid-state Z-mechanism composite photocatalyst in Next, the efficient conversion of H2O and CO2 into methane (natural gas) realizes the process of solar artificial photosynthetic fuel. The research paper is titled Visible-Light driven overall conversion of CO2 and H2O to CH4 and O2 on 3D-SiC @ 2D-MoS2 heterostructure. Published in J. Am. Chem. Soc. Artificial photosynthetic solar fuel refers to the process of converting water and carbon dioxide into chemical fuel through photocatalysis, photoelectric catalysis or electrocatalysis using renewable energy such as solar energy. This process simulates natural photosynthesis and is the way for humans to fundamentally solve energy and environmental problems. One is also a holy grail problem in the scientific world, facing huge challenges. There are several reactions in the process of artificial light synthesis of solar fuel. Among them, solar energy + CO2 + 2H2O → CH4 + 2O2 is a multi-step reaction involving 8 electrons, which is the most challenging reaction. Although the reaction has been reported in a large number of documents so far, the reaction effect is not ideal. In addition, although many literatures report the photocatalytic CH4 reaction in recent years, most of these reactions are obtained in the presence of sacrificial agents, and no release of oxygen is detected or the amount of oxygen detected is far below the stoichiometric ratio , So this is not the reaction of converting solar energy into chemical energy in the true sense. Therefore, the photocatalytic process of quantitatively oxidizing water to oxygen (or hydrogen peroxide) and at the same time efficiently reducing carbon dioxide to methane is the real conversion of solar energy into chemical energy. In response to this problem, this work constructed a marigold-type nano-flower with nano-crystals (3D-SiC) and two-dimensional nano-sheets (2D-MoS2) through electrostatic assembly technology, which has a two-type heterojunction and Z- scheme semiconductor configuration. This 3D-SiC @ 2D-MoS2 catalyst showed a methane yield of up to 323 μLg-1h-1 and an oxygen release of 620 μLg-1h-1 under visible light irradiation. Under 400 nm light, the photoconversion yield of methane reached 1.75% . This is the highest yield of total reduction of CO2 with pure water reported under visible light. Detailed product distribution analysis and isotope tracing experiments and mechanism studies show that with the oxidation of H2O, CO2 is gradually reduced to methane on the photocatalyst according to the hydrogenation pathway of CO2 → HCOOH → HCHO → CH3OH → CH4. It is worth noting that stoichiometric ratios of oxygen and methane can be detected during this research (oxygen / methane molar ratio is close to 2), and isotope experiments have also confirmed the generation of stoichiometric oxygen, which has the academic understanding and artificial photosynthesis. Important reference significance. This work provides a new way for artificially synthesizing solar fuel. Aluminum Extruded Profile,Aluminum Window Frame Profiles,Aluminum Window Frame Extrusions,Extrusion Aluminum Profile Guangdong Jihua Aluminium Co., LTD , https://www.gdaaluminiumprofile.com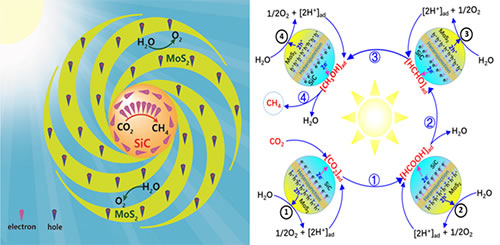
Dalian Chemical Research Institute and others made new progress in the research of artificial photosynthetic solar fuel