Wedge prism is an optical element having plane-inclined surfaces, usually the faces are inclined toward one another at very small angles. Wedges divert light toward their thicker portions.
Wedge prism is commonly used in laser system for eliminating the reflections from the second surface or for beam steering.circle wedge,square wedge,irregular wedge...Every materials,sizes,wedges and coatings may be available by custom orders. Standard and broadband antireflection coatings are available upon request.
optical wedges
Specification of our wedge prism as follow: Wedge Prism,Fused Silica Wedge Prism,Jgs1 Wedge Prisms,N-Bk7 Wedge Prism China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.opticsrealpoo.com
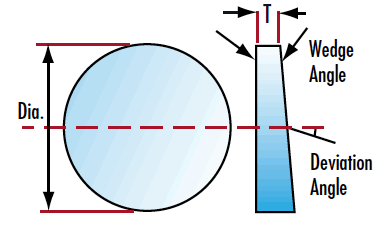
*Material: HK9L Grade A optical glass,Fused Silica JGS1,JGS2,JGS3, or other optical glass materials.
*Dimension Tolerance:+/-0.20mm to +0.01/-0.01mm
*Thickness Tolerance:+/-0.20mm to +/-0.005mm
*Surface Quality:80-50 to 10-5 Scratch/Dig
*Surface Flatness: at 632.8nm lambda to lambda /20 per 25mm
*Clear Aperture:80% -- 100%
*Angle Tolerance:3-5 minutes to 3 second
*Chamfer:0.3+/-0.20mm *45degree
*No Chamfer
*Coating Optional
Summary of specific classification problems of cameras
[ Pacific Security Network News ]
Cameras are very common in our daily lives, but the classification of cameras is not always clear. Let's talk about the classification of cameras today.
According to different sensor chips
We know that the sensor chip is the core component of the camera. At present, the sensor chips commonly used in cameras are ccd and cmos:
1.ccd camera, ccd is called a charge coupled device, ccd is actually just a way to organize the electrons coming out of the image semiconductor.
2.cmos camera, cmos is called "complementary metal oxide semiconductor", cmos is actually just a technology to put transistors on the silicon block, no more meaning.
Although ccd stands for "charge-coupled device" and cmos stands for "complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor", neither ccd nor cmos is useful for image sensing. Real-sensing sensors are called "image semiconductors", and ccd and cmos sensors are actually used. It is the same kind of sensor "image semiconductor". The image semiconductor is a pn-bonded semiconductor, and the photon explosion junction that can convert light becomes a proportional number of electrons. The number of electrons is calculated as the voltage of the signal. The more light enters the image semiconductor, the more electrons are generated, and the higher the voltage output from the sensor.
Because the human eye can see the target below 1lux illuminance (full moon night), the ccd sensor usually can see illuminance ranging from 0.1 to 3 lux, which is 3 to 10 times the sensitivity of the CMOS sensor, so the image quality of the current ccd camera. Better than cmos camera.
Cmos can integrate photosensitive elements, amplifiers, a/d converters, memories, digital signal processors and computer interface control circuits on a single piece of silicon. It has a simple structure, many processing functions, fast speed, low power consumption, low cost, etc. Features. The cmos camera has problems such as poor imaging quality, small size of the image sensitive unit, and low filling rate. After 1989, an "active image sensitive unit" structure appeared, which not only has the photosensitive element and the address sensitive switch, but also has a signal. Circuits such as amplification and processing improve photoelectric sensitivity, reduce noise, expand dynamic range, make some parameters similar to ccd cameras, and are superior to ccd in terms of function, power consumption, size and price, and gradually become widely used. . The cmos sensor can be made very large and has the same sensitivity as the ccd sensor, making it ideal for special applications. The cmos sensor does not require complicated processing to directly convert the electrons generated by the image semiconductor into a voltage signal, so it is very fast. This advantage makes the CMOS sensor very useful for high-frame cameras with high frame rates of 400 to 100,000 frames per second.
Divided by output image signal format
Analog camera
The analog camera outputs a standard analog video signal that requires a dedicated image capture card to be converted into digital information that the computer can process. Analog cameras are generally used in the field of television camera and surveillance. They have the characteristics of good versatility and low cost, but generally have low resolution, slow acquisition speed, and are susceptible to noise interference during image transmission, resulting in image quality degradation. Used in machine vision systems where image quality is not critical. Commonly used camera output signal formats are:
Pal (black and white is ccir), Chinese TV standard, 625 lines, 50 games
Ntsc (eia in black and white), Japanese TV standard, 525 lines, 60 games
Secam
S-video
Component transmission
Digital camera
The digital camera integrates the a/d conversion circuit internally, which can directly convert the analog image signal into digital information, which not only effectively avoids the interference problem in the image transmission line, but also removes the restriction of the standard video signal format. The signal output uses a more high-speed and flexible digital signal transmission protocol, which can be made into various resolutions, and the current situation of digital cameras is blooming. Common digital camera image output standards are:
Ieee1394
Usb2.0
Dcom3
Rs-644lvds
Channellinklvds
Cameralinklvds
Gigabit network
Divided by cell arrangement
The area array camera is a common form. The pixels are arranged neatly in rows and columns. Each pixel corresponds to a pixel on the image. The resolution we generally refer to refers to the number of pixels. It should be pointed out that the color image in our computer is generally represented by three values ​​of r, g, and b. However, our general color camera is not like this.
A black-and-white camera, where each pixel corresponds to a pixel, which has a relatively uniform sensitivity to light of various wavelengths, and only the gray value of each pixel is acquired.
A single-chip color camera converted by bayer. Each pixel of this camera actually corresponds to only one of r, g, and b. The three pixels of r, g, and b are arranged according to a certain rule. The obtained values ​​of the three primary colors r, g, and b of each pixel are calculated based on the three-color values ​​of the pixels and the surrounding points of the pixels, so that the images obtained by such cameras are often not obtained. Very good color effects, especially the corresponding edge position will have more obvious color distortion and loss of detail. At present, our common color cameras are generally in this form, and their price is similar to that of black-and-white cameras of the same grade.
Bayer color camera schematic
3ccd color camera, each pixel corresponding to three photosensitive elements r, g, b, using a prism to refract incident light to three ccd target surface, respectively, photoelectric conversion to get r, g, b three The color value (see the figure below). The image quality of such a camera is good, and there is no problem of loss of detail, but it is generally expensive due to the complicated structure of the camera. In addition, since the camera adopts a spectroscopic prism, the optical path of each light reaching each ccd target surface is different, so the lens needs to be designed in a targeted manner to achieve a better image effect, so a 3ccd camera is also needed. Equipped with a dedicated lens.
3ccd color camera schematic
Line camera
A line camera is a special form in which the pixels are arranged in a one-dimensional line, that is, there is only one line of pixels, and only one line of image data can be acquired at a time, only when the camera and the object move in the longitudinal direction. To get the 2D image we usually see. Therefore, in the machine vision system, it is generally used for the continuous movement of the measured object, and is particularly suitable for the case where the moving speed is fast and the resolution requirement is high.
The black and white camera is also the most commonly used line camera. Each pixel corresponds to a pixel, and the acquired grayscale image is obtained.
3line color camera, the camera has three rows of pixels of r, g, b, which are sensitive to light of three wavelengths of red, green and blue respectively, so each pixel point corresponds to the values ​​of three channels of r, g and b. Form color image data. It should be noted that since the three rows of pixels of r, g, and b are not collected at the same time (see the figure), motion correction is required in practical applications to obtain the desired color image.
Disclaimer: All works that indicate the source of this website are copyrighted or entitled to use by this website. Welcome to reprint and indicate the source. Non-this works are all from the Internet, and the purpose of reprinting is to transmit more information. It does not mean that this website agrees with its views and is responsible for its authenticity.