Type A-A coal columnar activated carbon: widely used in solvent recovery, industrial waste gas purification, protective equipment, home improvement air purification, power plant raw water purification, pure water treatment, power plant raw water treatment, electronic plant water treatment, chemical pigment water treatment, food factory And water treatment in pharmaceutical plants, as well as biological treatment of sewage plants, waste gas treatment in factories and garbage dumps, reuse of water, cultivation of seawater, etc., also in pure water production, sewage treatment, sewage biological carriers, marine aquaculture, and cold storage. Used in the fields of preservation, factory air purification, etc. Type B raw coal broken granular activated carbon: suitable for use in power plant raw water purification, especially in chemical wastewater filtration and purification, and power plant boilers using brackish water chlorine treatment, has a good treatment effect, and soil improvement of golf courses, etc. engineering. C type coal powdered activated carbon: mainly suitable for tap water purification, used to adsorb organic matter, residual chlorine and odor in raw water, reduce turbidity, improve taste and make it reach the standard of drinking water. This product also has good in sewage treatment industry. Processing effect. [Method for determination of oxygen-containing functional groups of activated carbon] About 0.1 g of a sample was added to the weighing bottle, and after vacuum drying at 110 ° C for 2 hours, the mass was measured. The sample was placed in a 100 mL Erlenmeyer flask and the mass of the empty weighing bottle was measured. 50 mL of a 0.1 mol/L aqueous sodium hydroxide solution was added to the Erlenmeyer flask, and the mixture was shaken at 25 ° C for 48 hours while performing a blank test of only 50 mL of sodium hydroxide having a concentration of 0.1 mol/L. Thereafter, the filtrate was filtered and 20 mL of a filtrate was taken, and a few drops of a methyl orange indicator was added thereto, and titration was carried out with an aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid having a concentration of 0.1 mol/L. Similarly, a 0.05 mol/L aqueous solution of carbonic acid and a 0.1 mol/L aqueous solution of sodium hydrogencarbonate were used for titration, and the amount of surface acidic functional groups was also determined by the above formula. From their difference, the ratio of the shuttle group, weak acid, and phenol hydrocarbon group can be calculated. Currently, Boehm titration can also be used for the characterization of oxygen-containing functional groups. Boehm titration is a method for the analysis of oxygen-containing functional groups of activated carbon proposed by HPBoehm. Qualitative and quantitative analysis is carried out according to the reaction of different strength bases with different surface oxygen-containing functional groups. It is generally believed that sodium bicarbonate neutralizes sulfhydryl groups, sodium carbonate neutralizes sulfhydryl groups and internal ketone groups, sodium hydroxide neutralizes saponins, internal vine groups and phenolic groups, and sodium ethoxide neutralizes sulfhydryl groups, internal ketone groups, and phenolic hydrocarbon groups. And carbon based. The content of the corresponding oxygen-containing functional group can be calculated from the amount of alkali consumed. Boehm titration is currently the most common method for surface chemical analysis of activated carbon. [Use activated carbon should pay attention to a few common sense] Activated carbon is a charcoal with a large specific surface area and a porous structure. According to its raw material classification, it can be divided into coal-based activated carbon, wood charcoal, shell charcoal and bone charcoal; according to its form, it can be divided into columnar carbon, broken carbon, powdered carbon and fibrous activated carbon. The main raw material of activated carbon is carbon, organic materials such as coal, wood, and husk, which are activated to form a complex pore structure with adsorption capacity. The pores having a radius greater than 20,000 nm are large pores, 150-20000 nm are mesopores, and less than 150 nm are micropores. The adsorption of activated carbon mainly occurs on these voids and surfaces. A large number of molecules on the pore walls of the activated carbon can generate strong gravitational force to attract impurities in water and air into the pores. The adsorption of activated carbon can be divided into physical adsorption and chemical adsorption. Physical adsorption occurs mainly in activated carbon-rich micropores for the removal of impurities in water and air. The molecular diameter of these impurities must be smaller than the pore size of activated carbon. Different raw materials and processing techniques result in different microporous structures, specific surface areas and pore sizes of activated carbon, which are suitable for different needs. The activated carbon contains not only carbon but also a functional group on its surface, which chemically reacts with the adsorbed substance, so that the adsorbed substance often occurs on the surface of the activated carbon. The impurities in the medium continuously enter the porous structure of the activated carbon through physical adsorption and chemical adsorption, so that the activated carbon is saturated and the adsorption effect is decreased. The activated carbon after adsorption saturation needs to be activated and regenerated, and its adsorption capacity is restored and reused. The adsorption performance indexes of activated carbon are mainly methylene blue value, iodine value and caramel adsorption value. The larger the adsorption capacity, the better the adsorption effect. Activated carbon can be used in air purification and feed water, wastewater treatment to separate or collect impurities in air and water media. Granular activated carbon and powdered carbon have the same effect and can be used for water treatment. Granular carbon is not easy to be lost, can be reused and reused, and is used for water treatment processes with light pollution and continuous operation. Powdered carbon is not easy to recycle, and is generally used for single-use use in intermittently polluted water treatment processes. The activated carbon of the feed water is generally developed with micropores and mesopores, and should meet three requirements: large adsorption capacity, fast adsorption speed, and good mechanical strength. Powdered activated carbon requires that in addition to the above characteristics, the smaller the particle size, the better the adsorption effect. Powdered activated carbon has a good application in the treatment of water smell and industrial pollutants. During the period from September to November 2005, due to the high content of odorant substances in Miyun Reservoir, Beijing No. 9 Water Plant of Tap Water Group adopted the technology of adding powdered carbon in the water pipeline to effectively remove the odor. During the pollution of nitrobenzene and benzene in the Songhua River, during the period of November 26-30, when the polluted water passed through Harbin, the Harbin Water Supply and Drainage Group under the guidance of the expert group of the Ministry of Construction used the technology of the ninth water plant to timely treat the water. Nitrobenzene meets water quality requirements. When using powdered charcoal, the adsorption test must be carried out according to the type and concentration of contaminants to be removed to determine the type of activated carbon and the amount of charcoal required. Before adding powdered charcoal, it should be noted that the carbon powder is made into a carbon slurry and uniformly added into the water. The longer the contact time, the better the decontamination effect. In the process of using powdered carbon, the following safety problems should also be paid attention to; when the concentration of dust reaches a certain proportion, it is easy to explode when exposed to open flame, so smoking, sparks and open flames are prohibited in the operation room; mixing with oxidant should be avoided; Light, should pay attention to dust pollution when using, the operator must be equipped with a dust mask to avoid inhalation into the lungs [Various applications of coal-based activated carbon] 1. Water treatment industry: tap water, industrial water, sewage treatment, purified water, beverages, food, medical water 2. Air purification: removing impurities, deodorizing, sucking, removing formaldehyde, benzene, toluene, xylene, oil and gas, etc. 3. Industry: Decolorization, purification, air purification 4. Fish farming: filtration 5. Reagents: catalyst and catalyst carrier
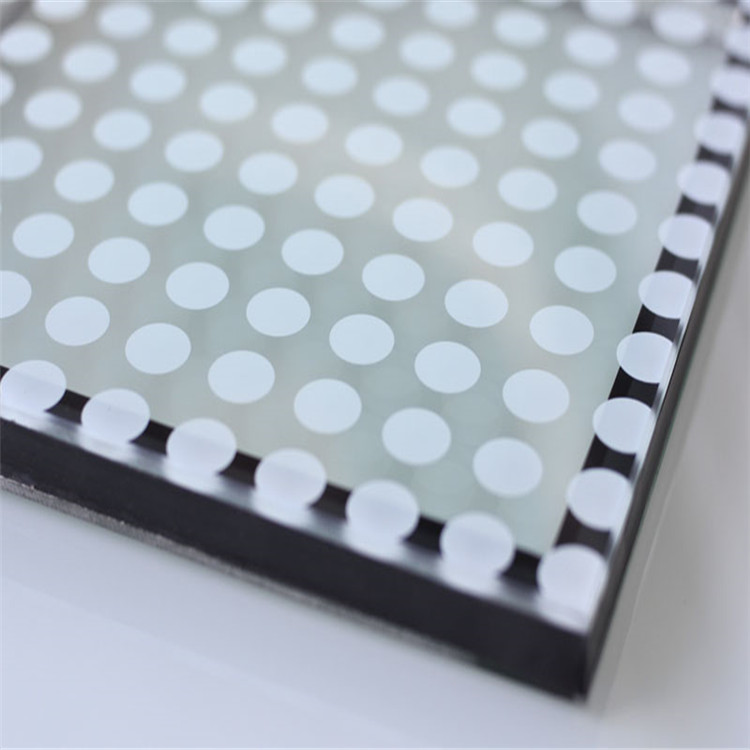
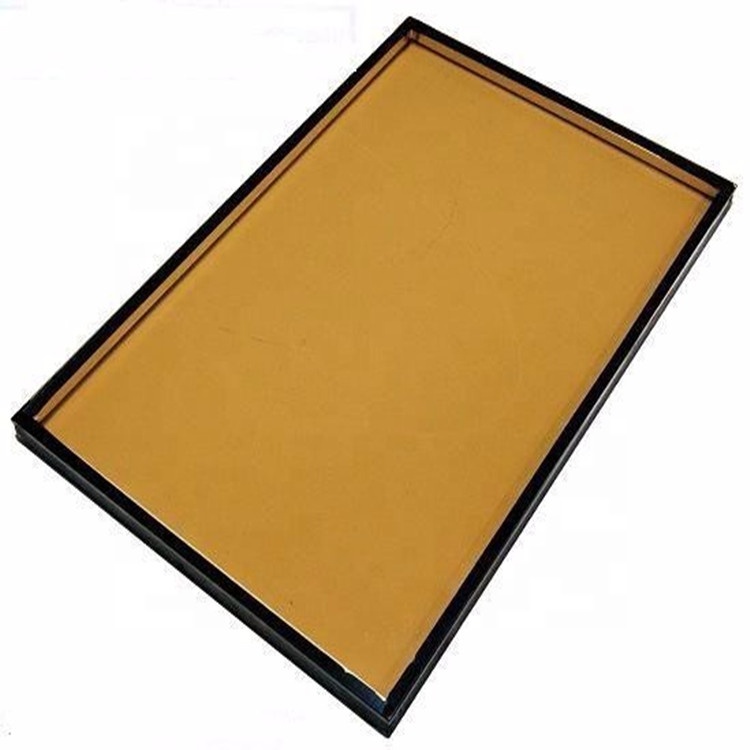
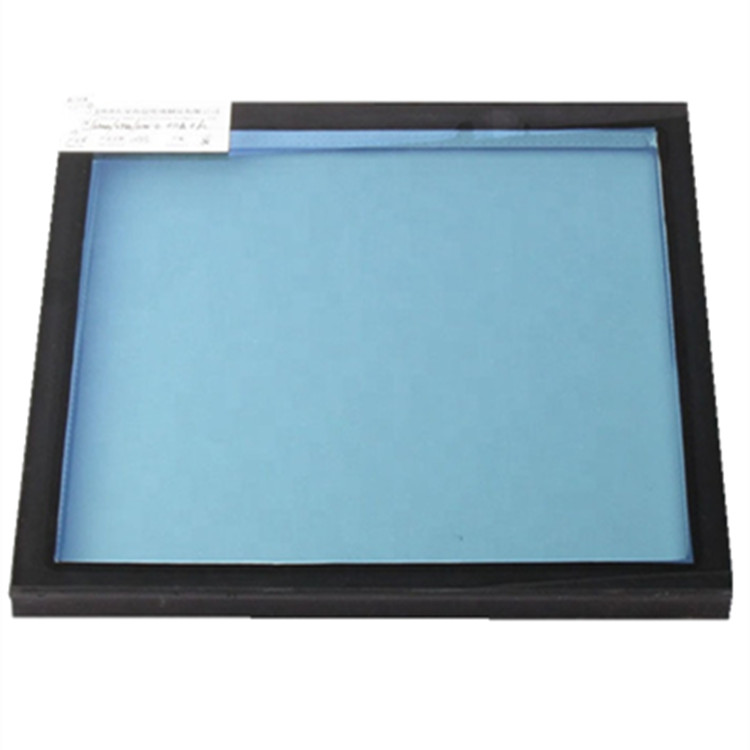
Insulating glass units, or IGUs, are designed to keep homes warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer. consists of twoor more glass window panes separated by a vacuum or gas-filled space to reduce heat transfer across a part of the building envelope. A wide variety of colored Insulated Glass options are available to you. Colored Insulated glass can be reached through Colored pvb Laminated Glass, colored tinted glass, reflective glass, low-e glass with color itself, sometimes, printed with some design also can match.
Insulated glass can be double insulated glass, triple insulated glass, laminated insulated glass, Low-E Insulated Glass, Vacuum Insulated Glass, insulated glass with internal blinds, colored insulated glass and so on for windows, doors, exterior curtain walls, thickness, color, size can be on customer's request.
IGU Glass,Curved Insulated Glass,Colored Insulated Glass,Double Insulated Glass Shanghai Lead Glass Co.,Ltd , https://www.leadglazing.com




Classification and action analysis of coal-based activated carbon